
Full resolution (JPEG) - On this page / på denna sida - N:o 5. Maj - Sidor ...
<< prev. page << föreg. sida << >> nästa sida >> next page >>
Below is the raw OCR text
from the above scanned image.
Do you see an error? Proofread the page now!
Här nedan syns maskintolkade texten från faksimilbilden ovan.
Ser du något fel? Korrekturläs sidan nu!
This page has never been proofread. / Denna sida har aldrig korrekturlästs.
the shortened cut-off. The maximum horsepower
is usually developed at piston speeds of 750 to
i.000 ft/min. The train resistance, on the other
hand, is high at starting, decreasing to a minimum
value at about five miles per hour, and then
increasing progressively with increase in speed.
This immediately suggests the possibility of two
limitations on the train load. The first, at starting,
with the locomotive developing its maximum
draw bar pull and a high train resistance; the
second, at a comparatively high speed, where the
draw bar pull of the locomotive has decreased
and the train resistance has increased to an equal
value. It is, of course, necessary to consider the
effect of grades and the ruling grade on a given
division determines the actual limit to train
tonnage. The ruling grade is one which cannot be
operated as a momentum grade, either because
of its length or approach, and limits the tonnage
by reducing the train speed to the stalling point.
It is therefore evident that the train load must
be determined on the basis of the necessary speed
for operating over the ruling grades of division.
Since the steaming capacity of the boiler does
not govern the draw bar pull, until speeds of
from 15 to 20 miles per hour are attained, it is
evident that at low speeds such as obtain in
passing over ruling grades, there is actually an excess
of boiler capacity. That is, the steaming capacity
of the boiler is greater than the power of the
cylinders and drivers to develop tractive effort.
This fact is the underlying principle in the
development of the locomotive booster.
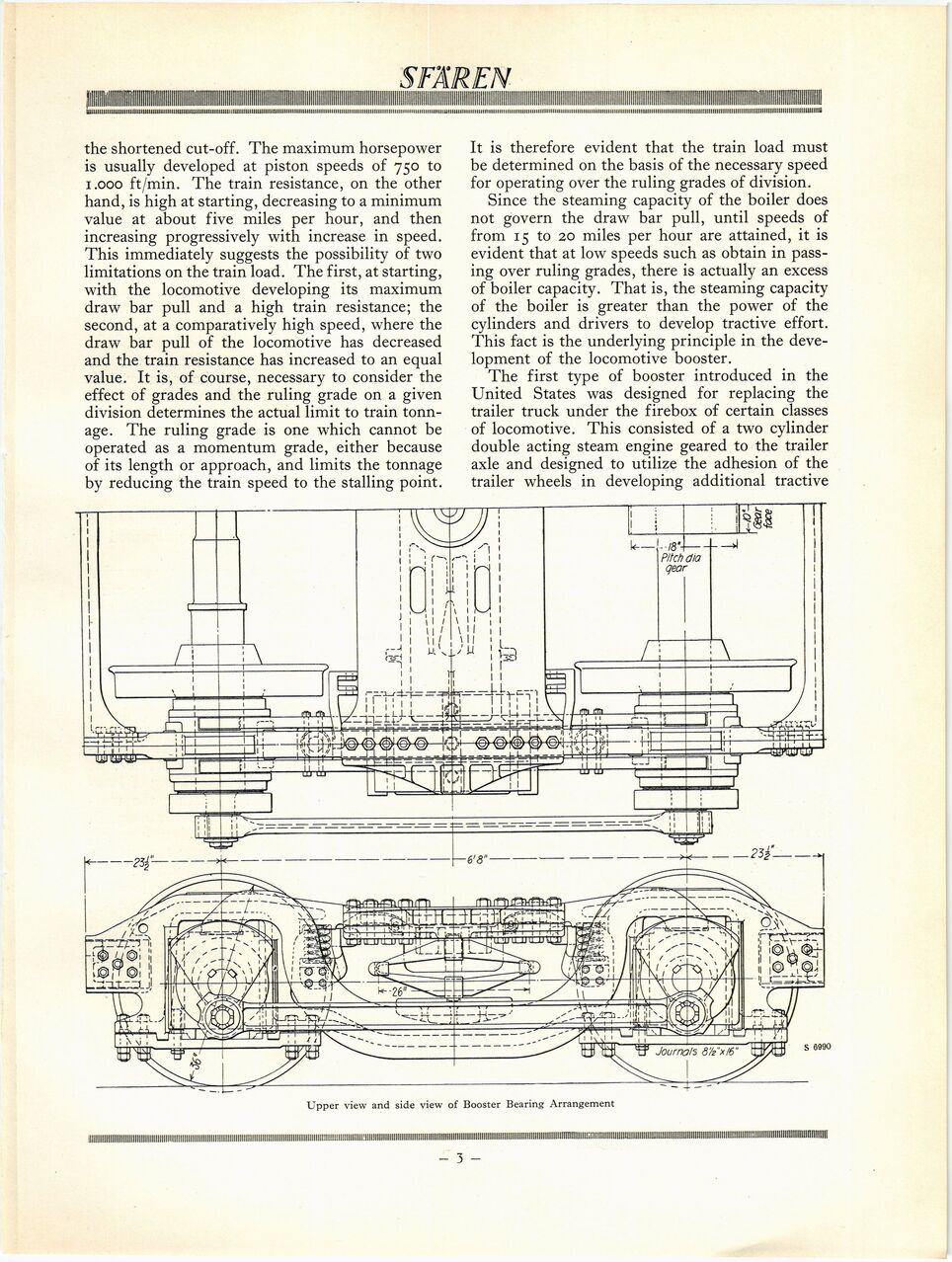
The first type of booster introduced in the
United States was designed for replacing the
trailer truck under the firebox of certain classes
of locomotive. This consisted of a two cylinder
double acting steam engine geared to the trailer
axle and designed to utilize the adhesion of the
trailer wheels in developing additional tractive
Upper view and side view of Booster Bearing Arrangement
<< prev. page << föreg. sida << >> nästa sida >> next page >>