
Full resolution (JPEG) - On this page / på denna sida - Geometry - Triangles
<< prev. page << föreg. sida << >> nästa sida >> next page >>
Below is the raw OCR text
from the above scanned image.
Do you see an error? Proofread the page now!
Här nedan syns maskintolkade texten från faksimilbilden ovan.
Ser du något fel? Korrekturläs sidan nu!
This page has never been proofread. / Denna sida har aldrig korrekturlästs.
GEOMETRY. 151
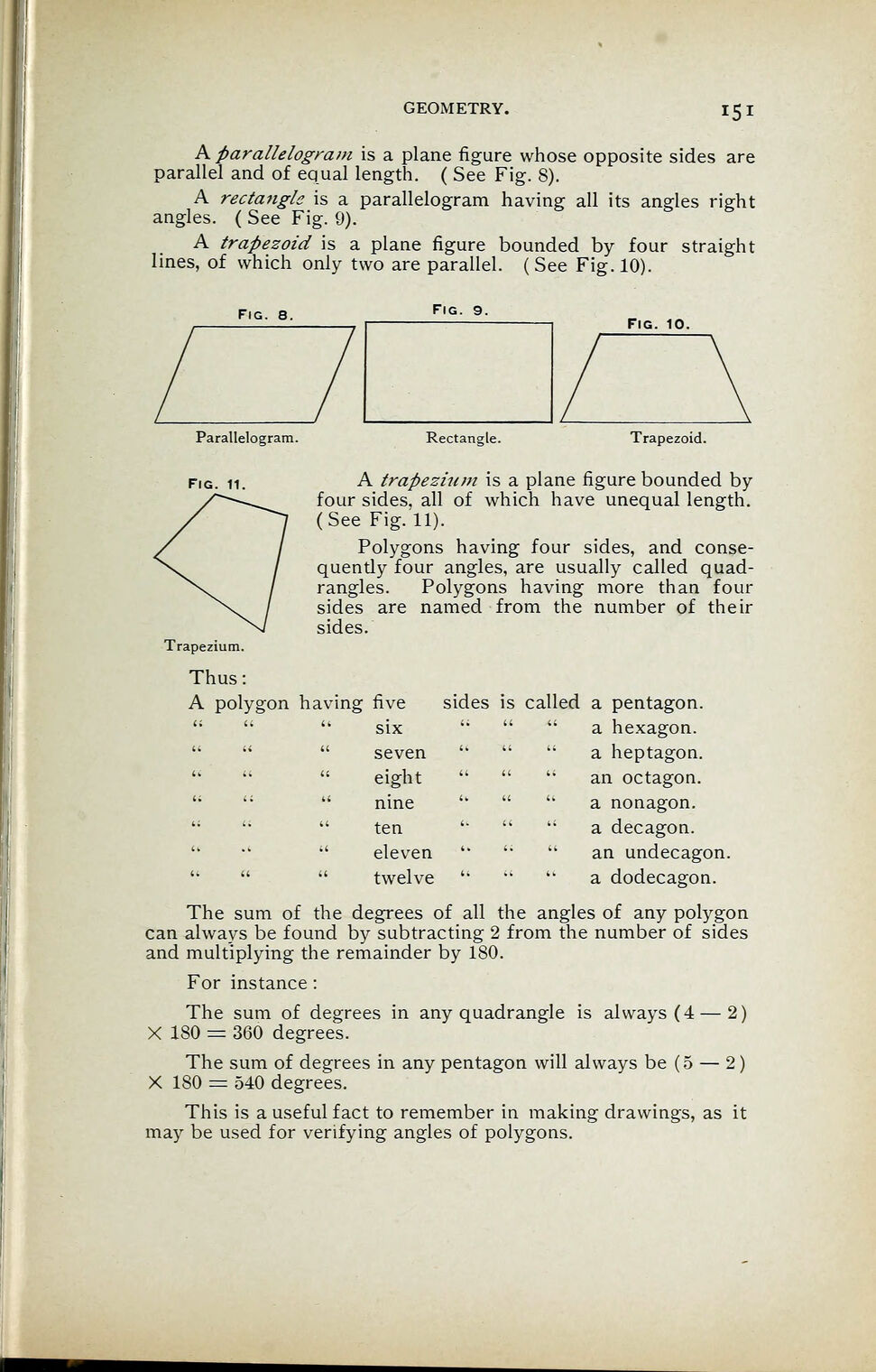
A parallelogram is a plane figure whose opposite sides are
parallel and of equal length. ( See Fig. 8).
A rectangle is a parallelogram having all its angles right
angles. ( See Fig. 9).
A trapezoid is a plane figure bounded by four straight
lines, of which only two are parallel. (See Fig. 10).
Fig. 8. Fig. 9.
Parallelogram.
Fig. 10.
Rectangle. Trapezoid.
Fig. 11. A trapezium is a plane figure bounded by
four sides, all of which have unequal length.
(See Fig. 11).
Polygons having four sides, and conse-
quently four angles, are usually called quad-
rangles. Polygons having more than four
sides are named from the number of their
sides.
Trapezium.
Thus
:
A polygon having five
" " six
" " seven
" " eight
’ ; " nine
" ten
" eleven
sides is called a pentagon.
" " a hexagon.
" "
a heptagon.
" " an octagon.
" "
a nonagon.
" "
a decagon.
’ ; " an undecagon.
twelve a dodecagon.
The sum of the degrees of all the angles of any polygon
can always be found by subtracting 2 from the number of sides
and multiplying the remainder by 180.
For instance :
The sum of degrees in any quadrangle is always (4 — 2)
X 180 = 360 degrees.
The sum of degrees in any pentagon will always be (5 — 2
)
X 180 = 540 degrees.
This is a useful fact to remember in making drawings, as it
may be used for verifying angles of polygons.
<< prev. page << föreg. sida << >> nästa sida >> next page >>