
Full resolution (JPEG) - On this page / på denna sida - Geometry - Trigonometry
<< prev. page << föreg. sida << >> nästa sida >> next page >>
Below is the raw OCR text
from the above scanned image.
Do you see an error? Proofread the page now!
Här nedan syns maskintolkade texten från faksimilbilden ovan.
Ser du något fel? Korrekturläs sidan nu!
This page has never been proofread. / Denna sida har aldrig korrekturlästs.
TRIGONOMETRY. 155
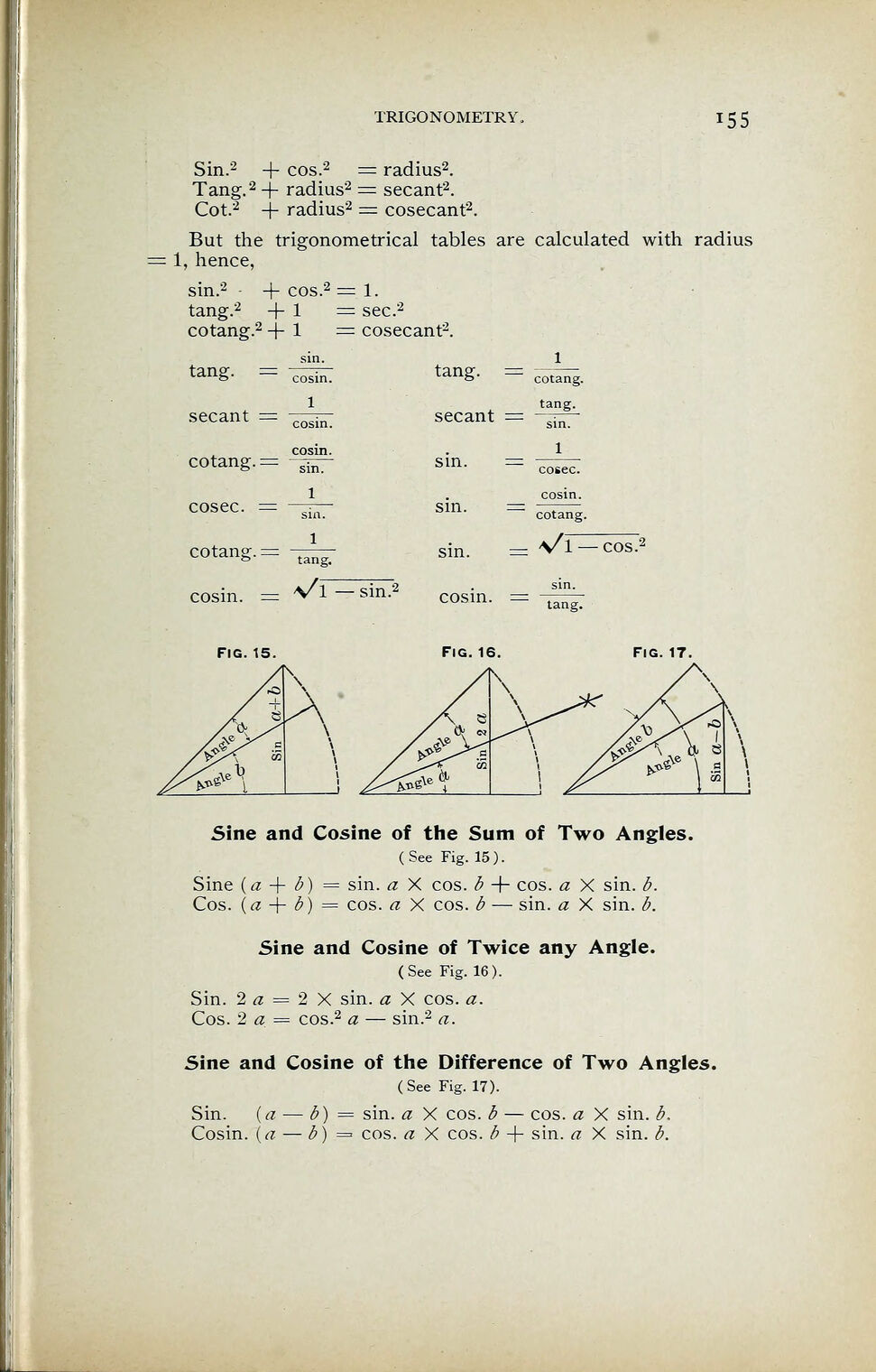
Sin.2
+ cos.2 = radius2
.
Tang. 2
+ radius2 = secant2
.
Cot.2
+ radius2 = cosecant2
.
But the trigonometrical tables are calculated with radius
= 1, hence,
sin.2
+ cos.2 = 1.
tang.2
+ 1 = sec.2
cotang.2 -j- 1 = cosecant2
.
tang. = cosin.
1
tang,
secant
secant — cosin.
cotang. = cosin.
sin.
1
sin.
cosec. — sin.
sin.
cotang. = 1
tang.
cosin. = */\ — sin.2
cosin.
cotang.
tang.
sin.
1
cosec.
cosin.
cotang.
_ vr=
tang.
FIG. 15.
/ +
\
\
/^\ 1
Fig. 16. Fig. 17.
6 \
Z&
<N
^\
^n >
(P.
X^H i
Sine and Cosine of the Sum of Two Angles.
(See Fig. 15).
Sine (a + b) = sin. a X cos. b -f- cos. a X sin. b.
Cos. (a -j- b) = cos. a X cos. b — sin. a X sin. b.
Sine and Cosine of Twice any Angle.
(See Fig. 16).
Sin. 2« = 2X sin. a X cos. a.
Cos. 2 a.
= cos.2
a — sin.2
a.
Sine and Cosine of the Difference of Two Angles.
(See Fig. 17).
Sin. {a — b) = sin. a X cos. b — cos. a X sin. b,
Cosin. (a — b) = cos. a X cos. b + sin. a X sin. b.
<< prev. page << föreg. sida << >> nästa sida >> next page >>